Introduction
Sometimes the process chain fails at particular step due to some kind of error and the “Repeat” option also
will not be applicable for the failed process. This article explains the steps for how to complete the process
chain and get the issue resolved.
Business Scenario
Step by Step Solution
The process chain fails at the step below while loading data into InfoProvider (marked in red box).
Process chain failure at this step is due to the erroneous records. It is necessary to manually correct it and
load data manually into the respective InfoProviders.
Once the data is loaded successfully at this step, start the process chain from next step onward as this step
is not required to execute again.
Finding the Variants and Instance of the Failed Process
Right-click the failed process. Select the Displaying Messages option.
Execute this, and the value of the other fields is returned: LOG_ID, TYPE, BATCHDATE and BATCHTIME.
Report to Execute Process Chain
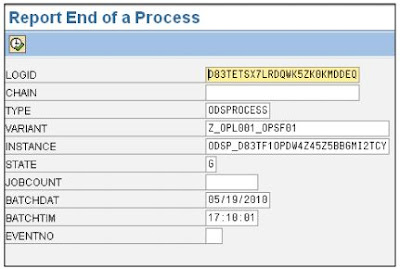
Go to the transaction SE38. Enter the program name - RSPC_PROCESS_FINISH and execute.
Enter the values in the fields received from above table. Additionally, make the STATE as „G‟ -> Execute.
Sometimes the process chain fails at particular step due to some kind of error and the “Repeat” option also
will not be applicable for the failed process. This article explains the steps for how to complete the process
chain and get the issue resolved.
Business Scenario
1. Data is loaded from R3 to BI using process chain. Variants involved in process chain are to load data
from R3 to different InfoProviders in BI.
2. Data is loaded successfully in one of the DSO (Z_OFCPS), but the process chain failed while further
data load to next DSO (Z_OPSF01).
3. This is because while doing the delta update, there are some erroneous records found and the process
chain failed.
4. Manual corrections are made on the erroneous records and uploaded data manually in the DSO
(Z_OPSF01).
5. The process chain is restarted from the One Step Ahead where it was failed as the manual corrections
are done and loaded data. Therefore, that step has to be skipped. (Also as process chain contains many
steps to be executed, and doing it manually is not a best practice.)
from R3 to different InfoProviders in BI.
2. Data is loaded successfully in one of the DSO (Z_OFCPS), but the process chain failed while further
data load to next DSO (Z_OPSF01).
3. This is because while doing the delta update, there are some erroneous records found and the process
chain failed.
4. Manual corrections are made on the erroneous records and uploaded data manually in the DSO
(Z_OPSF01).
5. The process chain is restarted from the One Step Ahead where it was failed as the manual corrections
are done and loaded data. Therefore, that step has to be skipped. (Also as process chain contains many
steps to be executed, and doing it manually is not a best practice.)
The process chain fails at the step below while loading data into InfoProvider (marked in red box).
Process chain failure at this step is due to the erroneous records. It is necessary to manually correct it and
load data manually into the respective InfoProviders.
Once the data is loaded successfully at this step, start the process chain from next step onward as this step
is not required to execute again.
Finding the Variants and Instance of the Failed Process
Right-click the failed process. Select the Displaying Messages option.
It will open the screen as below.
Copy the Variant and Instance from above screen.
Go to the transaction SE11. Select the table – RSPCPROCESSLOG.
Put the value for variant and instance received from above screen.
Report to Execute Process Chain
Go to the transaction SE38. Enter the program name - RSPC_PROCESS_FINISH and execute.
Enter the values in the fields received from above table. Additionally, make the STATE as „G‟ -> Execute.